The Lockheed Model 10, commonly known as the Electra, stands as a milestone in the era of early commercial aviation. This article traces the history, design innovations, and the lasting impact of the Lockheed Model 10 on how airlines carried people and mail across growing networks in the 1930s and beyond.
Key Points
- The Lockheed Model 10 introduced all-metal stressed-skin construction, increasing durability and reducing maintenance for advancing air travel.
- With a twin-engine, low-wing configuration, the aircraft offered greater range and reliability for early commercial routes.
- The distinctive twin-tail design and retractable gear improved stability, crew efficiency, and passenger comfort on longer flights.
- Airlines adopted the Model 10 to expand scheduled services, helping knit together regional networks during the 1930s.
- The Electra lineage influenced subsequent Lockheed designs and remains culturally linked to Amelia Earhart’s historic flights with the model.
History and Development of the Lockheed Model 10
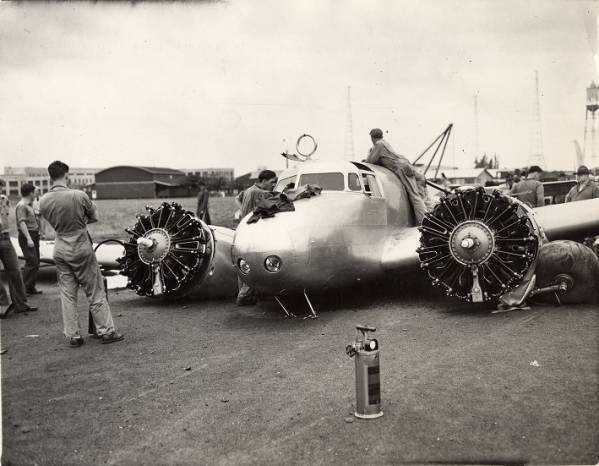

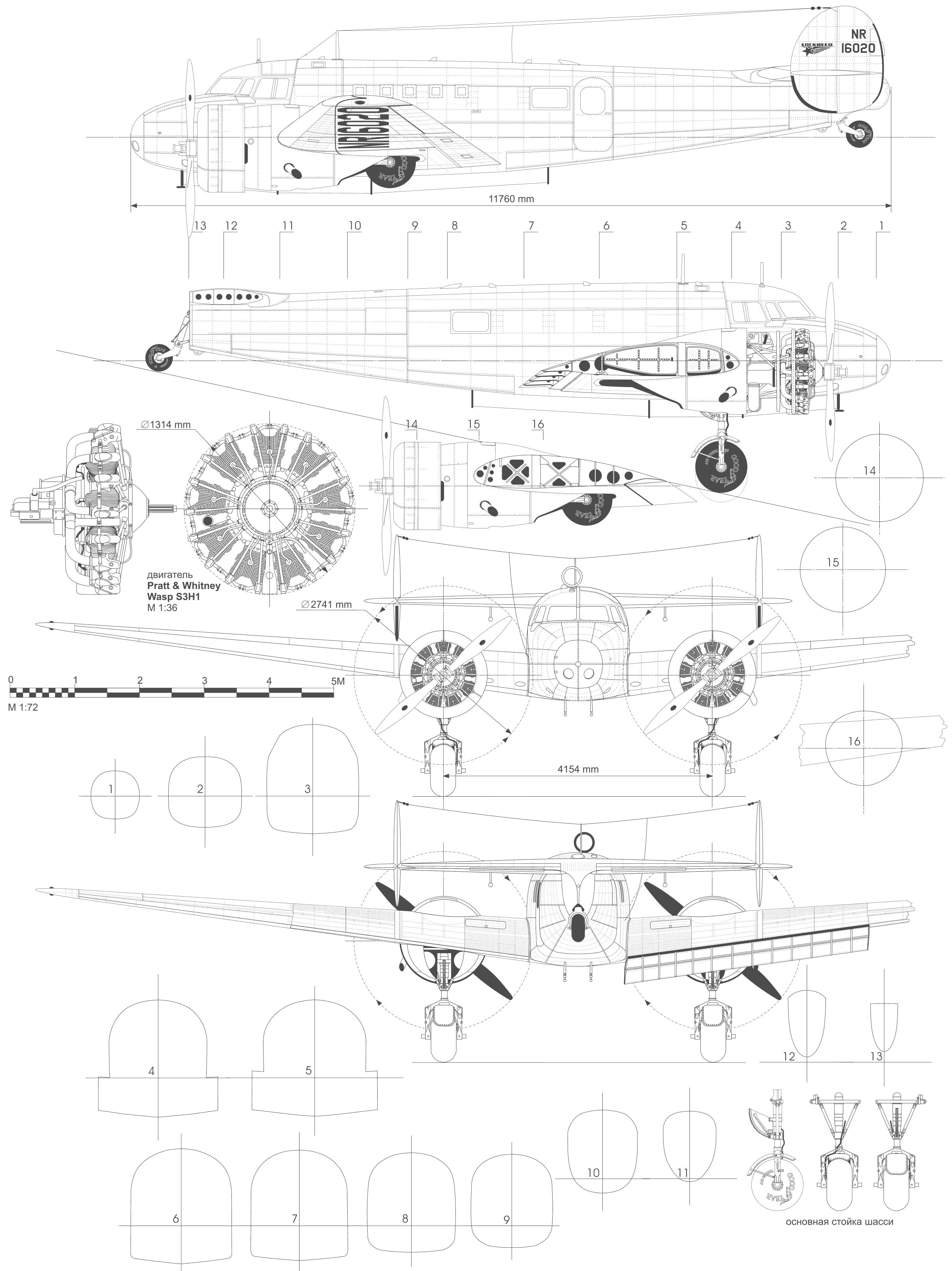
The development of the Lockheed Model 10 began in the early 1930s as Lockheed sought to rival emerging all-metal airliners. Engineers leaned into a twin-engine, low-wing profile to maximize reliability and speed for commercial operations. The aircraft first took to the skies in 1934 and soon entered service with several carriers, marking a turning point in how air travel could be scaled to meet rising passenger demand. The Electra program also showcased Lockheed’s growing capabilities in integrating advanced aerodynamics, dependable powerplants, and a cabin designed for practical airline use.
Design Features and Engineering Excellence
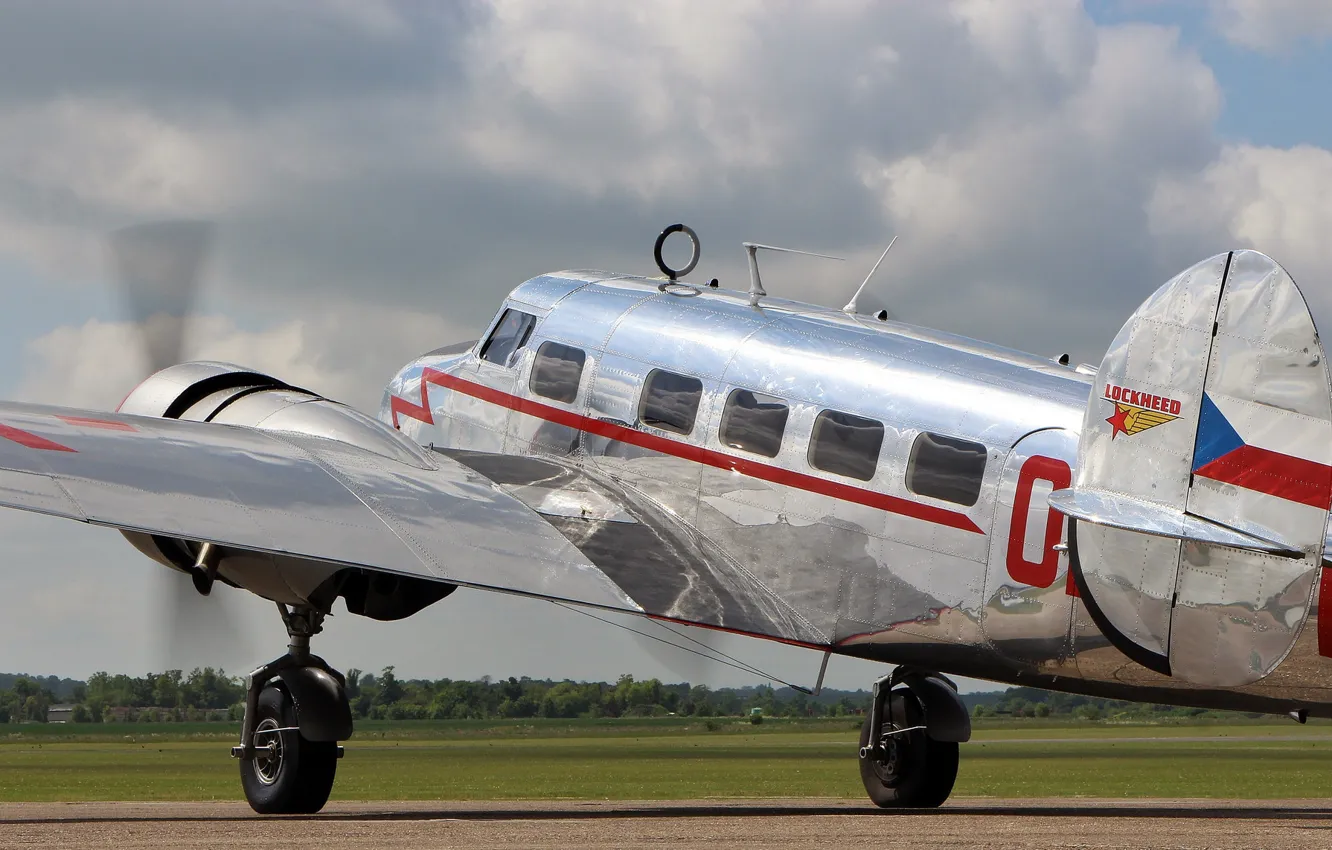

The Lockheed Model 10 combined several forward-thinking elements. Its low-wing, twin-engine layout provided a stable platform for smooth flight across a range of weather conditions. The airplane used an all-metal, stressed-skin construction technique, which made it lighter and sturdier than many wooden rivals of the era. A distinctive twin-tail configuration enhanced directional stability, while retractable landing gear reduced drag during cruise. Inside, the cabin was arranged to maximize passenger comfort and cargo practicality for regional and longer routes alike, signaling a shift toward more civilized air travel that could attract business and leisure travelers.
Operational Impact and Legacy
Across airlines, the Lockheed Model 10 helped accelerate the growth of scheduled air service, opening up new city pairs and enabling more predictable timetables. Its blend of performance, reliability, and passenger-friendly features set a standard that influenced later Lockheed designs and contributed to the broader industry move toward all-metal airliners. The aircraft also became part of aviation lore through its association with notable events, including Amelia Earhart’s use of a Lockheed Model 10 Electra for her world-record attempts, which cemented the family’s place in the history of flight.
When did the Lockheed Model 10 first fly and enter service?
+The Lockheed Model 10 first flew in 1934 and soon entered commercial service with a number of airlines, marking a turning point in practical, all-metal airliners.
What were the standout design features of the Lockheed Model 10?
+Key features included an all-metal stressed-skin construction, a low-wing twin-engine configuration, a retractable landing gear system, and a twin-tail arrangement that improved stability and handling for operators and pilots.
How did the Model 10 influence early commercial aviation?
+By demonstrating durable all-metal construction, improved aerodynamics, and passenger-focused cabin design, the Model 10 helped airlines expand routes and schedules, setting a template for future regional airliners and shaping industry expectations for speed, safety, and comfort.
Was Amelia Earhart flying a Lockheed Model 10 when she disappeared?
+Yes. Amelia Earhart was piloting a Lockheed Model 10 Electra during her ill-fated around-the-world attempt in 1937, a flight that remains a landmark in aviation history and a poignant reminder of the era’s pioneering spirit.
How many Lockheed Model 10 aircraft were built and who operated them?
+Several dozen Lockheed Model 10s were built, with major operators including American Airlines and other regional carriers. The model’s success helped Lockheed establish a strong foothold in the growing commercial aviation market of the era.