Ctla 4 Disease is a complex immunological condition arising from dysregulation of the CTLA-4 pathway, which helps keep the immune system in check. This definitive guide provides an accessible overview of what Ctla 4 Disease is, how it presents, how it is diagnosed, and the spectrum of treatment options available. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or clinician, understanding Ctla 4 Disease can empower better decisions and proactive care.
Overview
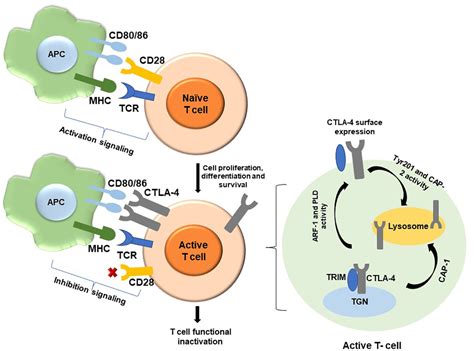
Ctla 4 Disease refers to disorders rooted in defects or dysfunction of the CTLA-4 signaling axis, which can lead to excessive immune activation or improper immune regulation. People with this condition may experience autoimmune-like symptoms, increased susceptibility to infections, and fluctuating clinical courses. The disease is often diagnosed through a combination of clinical history, genetic testing, and immune profile analysis, and management typically involves a multidisciplinary approach tailored to the individual.
Key Points
- Ctla 4 Disease encompasses a spectrum of immune dysregulation tied to CTLA-4 pathway abnormalities.
- Early recognition of warning signs can shorten diagnostic timelines and improve outcomes.
- Treatment often combines targeted therapies, immune support, and lifestyle adjustments.
- Genetic testing and family screening play important roles in identifying risk and guiding care.
- Ongoing research is expanding personalized treatment options for Ctla 4 Disease.
Symptoms and Warning Signals
Symptoms of Ctla 4 Disease vary widely, but common features may include autoimmune manifestations such as inflammatory symptoms in the skin, gut, or joints, along with signs of immune imbalance like recurrent infections or unusual responses to vaccines. Because presentations can mimic other immune or autoimmune conditions, a careful clinical evaluation is essential. If you notice persistent inflammatory symptoms, unexplained fatigue, or a family history of immune disorders, discuss Ctla 4 Disease with a specialist.
Causes and Risk Factors
Most cases of Ctla 4 Disease involve genetic changes that affect the CTLA-4 pathway, leading to altered immune control. Inherited variants can be passed through families, while some cases may arise from de novo mutations. Risk factors include a combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers that influence immune activation. Understanding the specific genetic landscape can guide prognosis and treatment choices.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Ctla 4 Disease typically involves a targeted workup: a detailed medical and family history, clinical examination for autoimmune and inflammatory signs, immunological assays to assess T-cell function, and genetic testing to identify CTLA-4–related abnormalities. A multidisciplinary team—often including immunologists, geneticists, and rheumatologists—helps interpret results and confirm a Ctla 4 Disease diagnosis while ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Treatment Options
Management of Ctla 4 Disease is individualized and may include immunomodulatory therapies, supportive care, and monitoring for potential complications. Treatments aim to rebalance the immune system, reduce inflammation, and prevent organ damage. Depending on the patient, clinicians may consider strategies such as targeted biologic agents, conventional immunosuppressants, vaccination planning, nutritional support, and rehabilitation services. Ongoing follow-up is essential to adjust therapy as symptoms evolve.
Living with Ctla 4 Disease
Living with Ctla 4 Disease involves proactive care, regular medical reviews, and a strong support network. Patients benefit from clear disease education, access to specialists, and strategies to manage stress, sleep, and infection risk. A personalized plan that includes emergency precautions, medication adherence, and lifestyle adjustments can improve quality of life and help individuals navigate day-to-day challenges.
Research and Future Directions
Current research for Ctla 4 Disease is expanding our understanding of CTLA-4 biology and identifying novel therapeutic targets. Clinical trials exploring precision medicine approaches, gene-based therapies, and combination regimens hold promise for more effective and tailored interventions in the years ahead.
What exactly causes Ctla 4 Disease and how is it inherited?
+Ctla 4 Disease typically arises from genetic variations that disrupt the CTLA-4 immune checkpoint, leading to dysregulated immune activation. In many cases, these genetic changes follow an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning a single copy of the altered gene can raise risk. However, the specific inheritance pattern can vary, and some cases occur due to de novo mutations with no family history.
How is Ctla 4 Disease diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically combines clinical assessment, immunological testing, and genetic analysis. A specialist will review symptoms, family history, and may order blood tests to evaluate immune cell function, followed by sequencing to detect CTLA-4–related mutations. Confirmation often requires a multidisciplinary interpretation of these findings.
What treatments are commonly used for Ctla 4 Disease?
+Treatments focus on restoring immune balance and preventing organ damage. Options may include targeted biologic therapies, traditional immunosuppressants, infection prevention strategies, and supportive care. The choice depends on symptom type, severity, patient age, and comorbid conditions, with regular monitoring to adjust therapy as needed.
Can Ctla 4 Disease be cured, or is it managed long-term?
+At present, Ctla 4 Disease is considered a chronic condition for many patients. Management aims to control symptoms, reduce flares, and maintain long-term health. Ongoing medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and, when appropriate, participation in clinical trials can help improve outcomes and quality of life.