Binary Transition Metal Phosphides are a versatile class of materials with applications in catalysis, energy storage, and electrocatalysis. However, researchers often stumble on avoidable mistakes that compromise performance and reproducibility. This article explores common mistakes with Binary Transition Metal Phosphides and what to avoid to ensure reliable results.
Common Mistakes With Binary Transition Metal Phosphides What To Avoid
Key Points
- Inadequate control of phosphorus stoichiometry can yield off-stoichiometric or mixed phases, skewing activity measurements.
- Misinterpreting XRD or other structural data due to peak overlap with oxides or phosphate byproducts.
- Phosphorus-containing materials are often air- and moisture-sensitive; proper handling and storage reduce degradation.
- Improper heating ramps or temperatures can cause decomposition or phase transitions in Binary Transition Metal Phosphides.
- Incomplete documentation of experimental parameters undermines reproducibility and data comparability.
Understanding Binary Transition Metal Phosphides
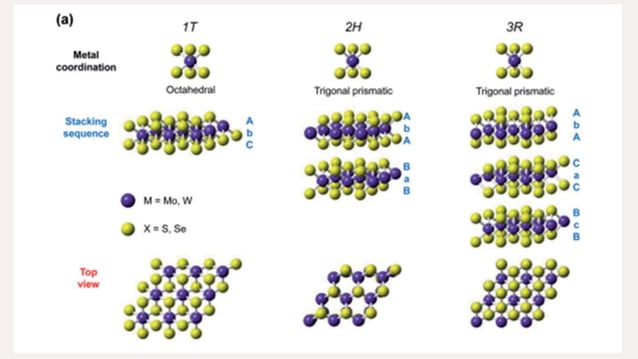
Binary Transition Metal Phosphides are compounds formed between a transition metal and phosphorus, typically exhibiting metallic conductivity and catalytic activity. In this class, the term “binary” emphasizes two elements: the metal and phosphorus. The precise stoichiometry and crystal structure govern properties such as electronic structure, surface chemistry, and stability. Being aware of common phase diagrams helps anticipate which phases can form under different synthesis conditions.
Synthesis and Handling Pitfalls for Binary Transition Metal Phosphides
When forming Binary Transition Metal Phosphides, the choice of precursor materials, their purity, and the phosphorus source all influence the final phase. Common mistakes include using impure phosphorus sources, neglecting the atmosphere, or skipping activation steps. Controlling the atmosphere, temperature profile, and phosphorus balance reduces the risk of impurities and off-target phases.
Characterization and Data Interpretation for Binary Transition Metal Phosphides
Characterization challenges for Binary Transition Metal Phosphides include differentiating between close-lying phases and recognizing surface oxides that can mask true composition. Rely on multiple techniques (XRD, SEM/TEM, XPS) and compare against well-established references. Calibration and instrument settings are essential to avoid misassignment of phases.
Storage, Stability, and Safety for Binary Transition Metal Phosphides
Phosphides can be reactive with air or moisture, which may form oxide surfaces or degrade the material. Store under inert conditions if possible, and handle phosphorus-containing materials with appropriate PPE and waste protocols. Safety data sheets and institutional guidelines should guide disposal and spill response.
Reporting and Reproducibility for Binary Transition Metal Phosphides
Transparent reporting for Binary Transition Metal Phosphides includes exact precursor masses, heating ramps, gas flow or pressure, and quenching protocols. Reproducibility improves when researchers share detailed characterization conditions and data analysis workflows, enabling others to replicate results accurately.
What defines Binary Transition Metal Phosphides and where are they most commonly used?
+Binary Transition Metal Phosphides are compounds of a transition metal with phosphorus, typically forming a single P-containing phase. They are widely explored in catalytic applications (e.g., hydrogen evolution, hydrodesulfurization) and energy storage due to their conductivity and active sites.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What is a frequent mistake when synthesizing Binary Transition Metal Phosphides?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>A common error is poor control of phosphorus content or incomplete phase formation, leading to mixed phases that misrepresent catalytic activity or stability.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can I verify phase purity and composition in Binary Transition Metal Phosphides?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Use complementary techniques such as X-ray diffraction with proper reference patterns, electron microscopy for morphology, and surface analysis like XPS; corroborate findings across methods to avoid misinterpretation.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What safety considerations should I keep in mind with phosphorus-containing materials?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Phosphorus compounds can be reactive with air and moisture and some phases may be pyrophoric. Work in a ventilated hood, use inert atmospheres when required, and follow waste disposal guidelines.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can I improve reproducibility in studies of Binary Transition Metal Phosphides?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Document all synthesis parameters (precursor masses, ramps, gas composition, and temperatures), report full characterization data, and provide access to raw datasets when possible to enable independent verification.</p>
</div>
</div>