Binary Metal Phosphide is redefining energy storage materials. In this article, the term Binary Metal Phosphide is used to describe two-element compounds formed from a metal and phosphorus, and we explore why these materials offer exceptional energy storage performance. By tuning composition and structure, Binary Metal Phosphide can achieve high electron conductivity, stable interfaces, and flexible voltage windows that suit lithium-, sodium-, and beyond-ions chemistries.
What is Binary Metal Phosphide?
Binary Metal Phosphide refers to compounds made from a metal (for example Fe, Co, Ni) and phosphorus in a simple two-element formula. In energy storage, these materials frequently appear as metal phosphides such as FeP, CoP, or NiP, where the interaction between metal d-electrons and phosphorus p-states promotes fast charge transfer and structural stability. The term Binary Metal Phosphide underscores the binary, two-component nature that supports straightforward synthesis and scalable performance tuning.
Unlocking Superior Energy Storage Performance with Binary Metal Phosphide
Several properties converge to boost performance in devices. Binary Metal Phosphide materials often exhibit high intrinsic electrical conductivity, favorable redox activity, and resilience to volumetric changes during cycling. The lattice can accommodate ion insertion with less distortion, while tailored surface chemistries stabilize the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI). These features translate into higher rate capability and longer cycle life across Li-, Na-, and multivalent chemistries.
Key Points
- High electronic conductivity and fast charge transfer support superior rate performance.
- Adjustable stoichiometry and phase structure enable optimization of voltage windows and energy density.
- Structural robustness minimizes capacity fade caused by volume changes during cycling.
- Scalable synthesis routes and compatible supports facilitate practical material deployment.
- In situ insights into phase evolution guide reliable design rules for long-term stability.
Design and Synthesis Strategies
To maximize the advantages of Binary Metal Phosphide, researchers pursue morphology control, nanoscale architectures, and composite integration. Approaches include controlled phosphidation, carburization, and carbon-based scaffolds to improve conductivity, as well as doping strategies to tune electronic structure. Emphasizing scalable methods—such as spray pyrolysis, ball milling followed by phosphidation, and solid-state routes—helps bridge laboratory success with real-world applications. Embracing surface engineering and protective coatings further extends device life in harsh electrolytes.
Applications in Energy Storage Devices
Binary Metal Phosphide in Lithium- and Multivalent-Ion Batteries
In lithium- and multivalent-ion systems, Binary Metal Phosphide acts as a high-rate cathode or anode, depending on the phase and integration. Its redox-active phosphorus mechanism can contribute to extra capacity, while the metal network supports rapid electron transport. When used as a composite with carbon, it delivers a balance of power and energy density.
Binary Metal Phosphide in Sodium-Ion and Beyond
For sodium-ion and emerging chemistries, the adaptable lattice and low diffusion barriers of many binary phosphides enable effective Na insertion/extraction and high-rate performance. Tailoring the particle size and porosity helps accommodate larger Na ions and improves electrolyte accessibility.
Device Architecture and Practical Considerations
Successful deployment often requires synergy with conductive matrices, stable SEI formation, and compatibility with existing electrolytes. Binary Metal Phosphide-based electrodes are frequently integrated with carbonaceous hosts or 3D current collectors to maximize utilization and minimize resistive losses. Safety, cost, and manufacturing scalability remain important considerations as researchers scale toward commercial cells.
Challenges and Future Outlook
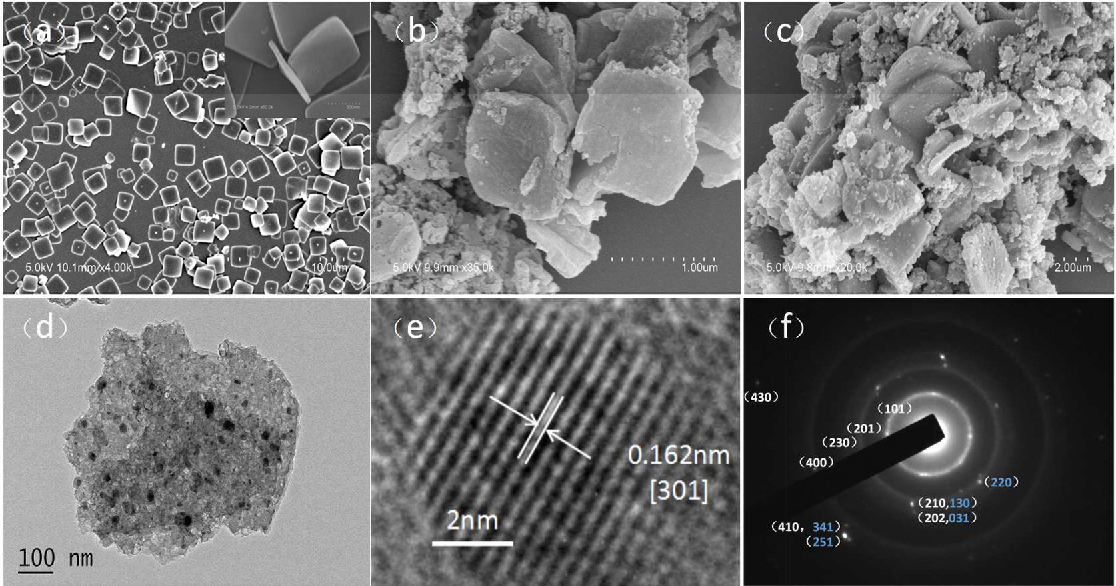

Key challenges include controlling phase stability during cycling, managing synthesis costs, and ensuring compatibility with high-voltage electrolytes. Ongoing research focuses on in situ characterization, computational design, and environmentally friendly processing to accelerate translation from lab to industry.
What makes Binary Metal Phosphide different from other metal phosphides?
+Binary Metal Phosphide refers specifically to two-element systems with a direct metal–phosphorus composition, enabling simpler synthesis routes and tunable properties. The binary nature often yields more predictable phase behavior and enhanced conductivity, which can translate into better rate performance and scalability compared with more complex phosphide families.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How does Binary Metal Phosphide improve cycle life in batteries?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Cycle life is improved by the lattice flexibility and robust interfaces of many binary phosphides. When integrated with conductive carbon and stabilized SEI layers, these materials resist volume changes and suppress aggregated degradation, leading to slower capacity fade over hundreds to thousands of cycles.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there challenges with scaling up production of Binary Metal Phosphide materials?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Challenges include achieving uniform phase purity at large scales, controlling particle size distribution, and integrating with standard electrode processing. However, scalable methods such as scalable phosphidation and composites with carbon matrices are active areas of development to address these concerns.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Which energy storage devices benefit most from Binary Metal Phosphide?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Devices that demand high power and good cycling stability, such as high-rate Li- and Na-ion batteries and supercapacitor-like hybrid systems, benefit notably. While Li-based devices are common, emerging Na-, K-, and multivalent chemistries can also leverage the fast kinetics of Binary Metal Phosphide materials.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can researchers accelerate development of Binary Metal Phosphide-based materials?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Acceleration comes from combining computational screening with high-throughput synthesis and in situ/ex situ analysis. Standardized electrochemical testing and accelerated aging protocols help identify promising compositions and architectures more rapidly.</p>
</div>
</div>